 Meningitis is an infection caused by either a viral or bacterial infection. It causes an inflammation of the meninges, which is the membrane which covers the brain and the spinal cord. This can be very serious if left untreated. In babies and young children, death can occur in a matter of hours in some serious cases. Therefore it is advised to get medical help as soon as possible if you suspect that your child or patient has meningitis.
Meningitis is an infection caused by either a viral or bacterial infection. It causes an inflammation of the meninges, which is the membrane which covers the brain and the spinal cord. This can be very serious if left untreated. In babies and young children, death can occur in a matter of hours in some serious cases. Therefore it is advised to get medical help as soon as possible if you suspect that your child or patient has meningitis.
There are different types of this infection, and some can be vaccinated against. For example, there is a Meningitis B vaccine which protects against some meningitis-causing bacteria. The vaccine is given to babies when they are 8 and 16 weeks old, with a booster at age 1.
Signs and Symptoms of Meningitis
- Cold hands and feet
- Stiff neck, limb and joint pain
- Pallor or mottling skin
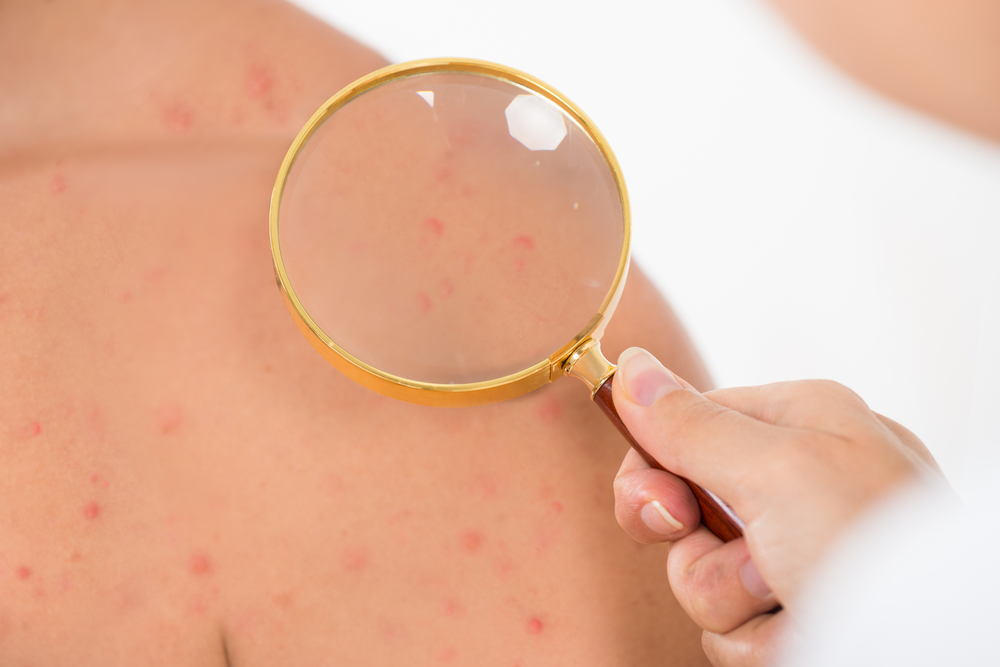
- Rash that does not fade with glass test
- Drowsiness
- Headaches
- Photosensitivity (not liking bright lights)
- Fever
- Vomiting
The glass test (in which the red spots do not vanish when a glass is rolled over the skin) is one of the last and most serious signs. If you see this, it is vital you get help as soon as possible. Tell the Emergency Medical Services what you think is wrong as meningitis is easy to confuse with other common illnesses. A survey showed that 50% of children with meningitis were initially sent home when taken to a Doctor.
For more information on training courses, visit our “Courses” page which also includes our First Responder and First Person on Scene (FPOS) Courses.


Pingback: Meningitis and a real Life story on what it is like to have meningitis